What is CAD software?
CAD (Computer Aided Design), also called 3D modeling, allows engineers and designers to build realistic computer models of parts and assemblies for complex simulations and digital manufacturing. Models created with CAD can be produced as physical components with 3D printing, CNC machining and injection molding.
CAD software can simulate a wide range of parameters, including strength or temperature resistance before any physical models have been created. Using CAD software enables you to work faster and more cost-efficiently, without compromising on the quality of your components.
What is solid modeling?
Solid modeling creates solid 3D models as if they are actual parts, with a logical workflow that’s similar to the processes which would be used to manufacture the part. Some of these operations include extruding, drilling and threading. Solid models can intersect, join and subtract objects from one another to create the desired part.
Another advantage of solid modeling is that it’s usually parametric, meaning that changes or parameters are saved at every stage of the modeling process and can be edited at any time. This allows features of the model to be quickly modified without needing to create the part from scratch.
Assembly modeling is an important stage in solid modeling, allowing individual parts to be assembled together, forming complex models. Assemblies can be used to insert standard components such as fasteners or bearings, that have been downloaded directly from the manufacturers. Motion elements can also be applied to assemblies, allowing detailed motion analysis to be used to evaluate the mechanical performance of the design.

What is surface modeling?
Surface modeling is usually used for more aesthetic features of a product. It is much easier to create more organic and free-form geometry using this type of CAD software. Many of the constraints found in solid modeling are not an issue with surface modeling, however, this comes at a cost of sometimes being less accurate.
As the name suggests surface modeling only deals with the surfaces of the part, with no solid interior. However, once the part has enough surfaces to close the part, it can be filled and then used for 3D printing. When developing designs using surface modeling, it can be hard to go back and make changes because usually, it’s not parametric.
Each type of modeling software has benefits and drawbacks, depending on the type of design being produced this needs to be considered. Sometimes using both solid and surface modeling is needed to combine the benefits of each.
What is sculpting (organic modeling)?
Sculpting, or organic modeling, is mainly used for creating freeform surfaces with intricate details such as characters, jewelry or organic shapes found in nature.
Sculpting software packages such as Pixologic’s ZBrush or Autodesk’s Mudbox were designed with classical sculpting in mind. They allow digital sculptors to start from a simulated ball of clay and use a pressure-sensitive drawing tablet or monitor to manipulate their object with brushes that reflect classic sculpting tools for moving, adding or removing material from their object.
Using these tools, artists can create sculptures that consist of tens of millions of polygons that capture even the most intricate details.
What’s the best CAD software for 3D printing?
There are many CAD programs to choose from, each with its own advantages and industry niches. Let’s break down the most common CAD software options by their principal benefits and common file types.
| Software | Description | Common File Type |
|---|---|---|
 |
Solidworks is industry-standard engineering software used for part and assembly modeling. It includes simulation features as well as drawing and assembly tools. | .sldprt .sldasmslddrw |
 |
Autodesk AutoCAD, a software package for 2D and 3D CAD, is used across a wide range of industries, by architects, project managers, engineers, graphic designers and many other professionals. | .dwt .dwg |
 |
Inventor has very similar features to Solidworks, with professional 3D mechanical design, drawing tools and product simulation tools. | .ipt .iam .idw |
 |
Autodesk Fusion 360 is similar to Solidworks, with the addition of integrated manufacturing tools and sculpting tools. It’s also available for free for students, enthusiasts, hobbyists and startups. | .f3d |
 |
Sketchup is an entry-level software that’s easy to use but comes with basic features. It’s mainly used for applications such as architectural models and interior design. | .skp |
 |
Solid Edge provides solid modeling, assembly modeling and 2D orthographic view functionality for mechanical designers. Solid Edge is a direct competitor to SolidWorks, PTC Creo and Autodesk Inventor. | .prt .asm |
 |
PTC Creo is a suite of design software with a focus on product design for discrete manufacturers. The suite consists of apps, each delivering a distinct set of capabilities within product development. | .prt .asm |
 |
Onshape is a full online CAD software package. It makes extensive use of cloud computing, with compute-intensive processing and rendering performed via servers. | Cloud Only |
 |
Rhino is a multi-use, freeform surface modeler for engineering, architecture and jewelry design. | .3dm |
 |
ZBrush is a digital sculpting tool that combines 3D/2.5D modeling, texturing and painting. The main difference between ZBrush and more traditional modeling packages is that it’s more akin to sculpting. | .obj |
 |
Autodesk 3ds Max is a professional 3D computer graphics program for making 3D animations, models, games and images. | .3ds .max |
All of these CAD programs can output STL or OBJ files for 3D printing, as well as STEP and IGES for CNC manufacturing.
What CAD programs are professionals using?
In developing this article, we sent a survey to over 750 designers and engineers who’ve used Protolabs Network to see which CAD software they prefer. Let’s explore the results.
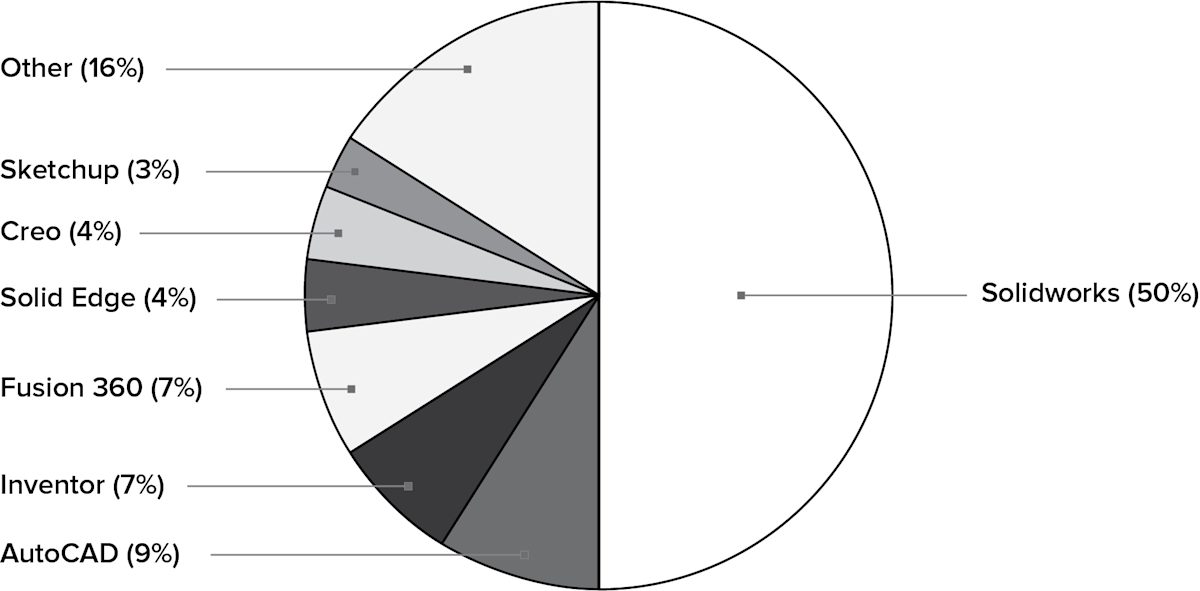
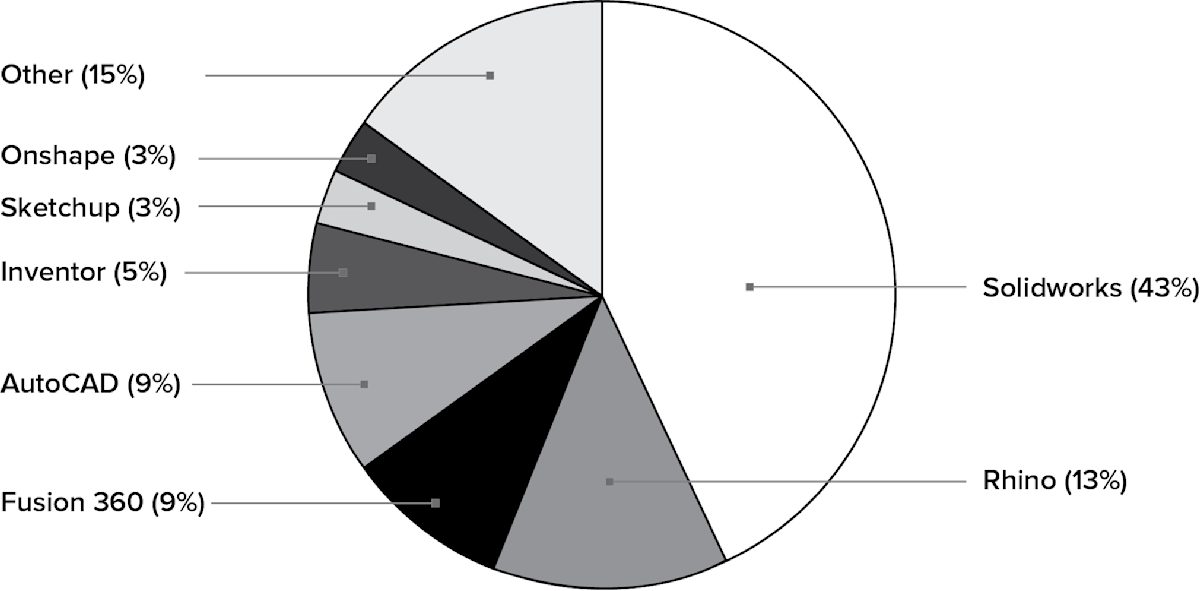
The survey found that the majority of engineers and designers use Solidworks for CAD design. Engineers tended to prefer AutoCAD, Inventor and Fusion 360 (the only free professional CAD software package on the list), while Rhino proved to be the second most popular modeling tool for designers. Interestingly enough, Rhino did not appear on the list for engineers even though it ranked highly for designers.
Ready to start 3D printing your CAD designs?
Our 3D printing services Upload your CAD file for a free, instant quote
Frequently asked questions
What’s the most common CAD software?
While there are a ton of CAD programs available today, the most common is still AutoCAD. It’s one of the oldest and most popular software for 3D design and drafting.
What’s the best free CAD software?
If you don’t have access to more pricey enterprise software for CAD modeling, you can use free options like Fusion 360 and SketchUp Free.
What’s the best CAD software for 3D printing?
The most powerful software for 3D printing you’re likely to find is Autodesk Fusion 360, which makes it a preferred choice for designers, engineers and architects. It’s ideal for designing and producing very efficient mechanical components, to name one of its many benefits. You also have AutoCAD, the industry mainstay used by engineers and designers across nearly every industry.
Aside from these two, another viable software is nTopology. Targeted more toward academic and professional users, it lets you create design processes instead of building up objects from scratch, which makes optimizing your parts that much more efficient.
Can Protolabs Network create 3D files from my designs?
While Protolabs Network can provide DFM analysis on your CAD files and technical drawings, we can't create digital models for you based on drawings of your part or physical components.