CNC machining
How do you define CNC (computer numerical control) machining and what are the different types of machines out there? Learn how milling and turning machines work, improve your designs for CNC processes, dive deeper into technical parameters like drill bit sizes and thread types and see what you can create with CNC machining. And did you know you can source CNC parts locally and globally? Head to our local sourcing page for more info.

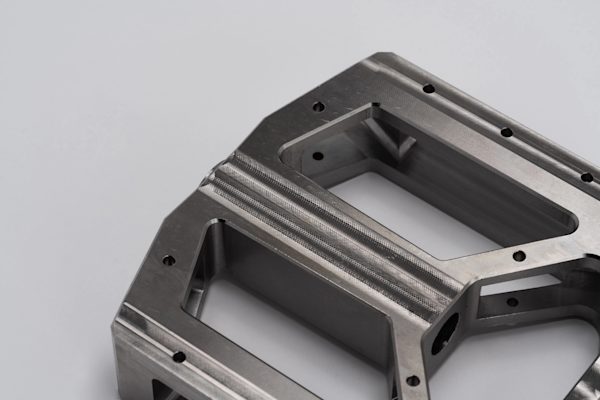
The advantages of 5-axis CNC machining
Five-axis CNC machining gives engineers a lot more freedom when it comes to making complex, high-precision parts. Instead of cutting from one direction at a time, the machine can pivot and rotate the tool or part to reach tricky angles. That means fewer setups, smoother finishes, and more design possibilities. In this article, we’ll break down how it works, when to use it, and how to make the most of it in your next project.

CNC machining for small parts
Learn how to design and manufacture CNC small parts with tight tolerances, the right materials, and reliable DFM practices.

A guide to acrylic CNC machining
Discover everything about acrylic CNC machining: material grades, design guidelines, surface finishes, applications, and cost factors for precision PMMA parts.
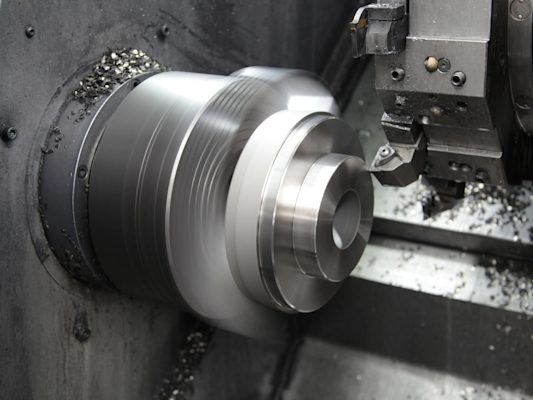

CNC turning machines: How they work and when to use them in manufacturing
Learn how CNC turning machines work, their applications, and when to choose turning vs. milling. Complete engineering guide for cylindrical parts
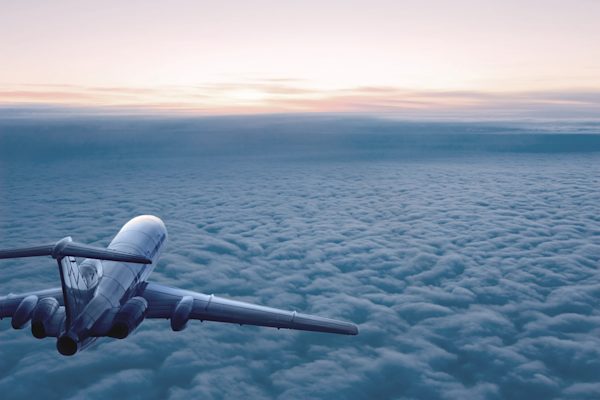

Precision CNC machining for aerospace applications
From launching satellites and manufacturing autonomous aircraft to fine-tuning flight systems, aerospace teams need parts that perform without compromise. CNC machining powers ideas that are ready for takeoff.
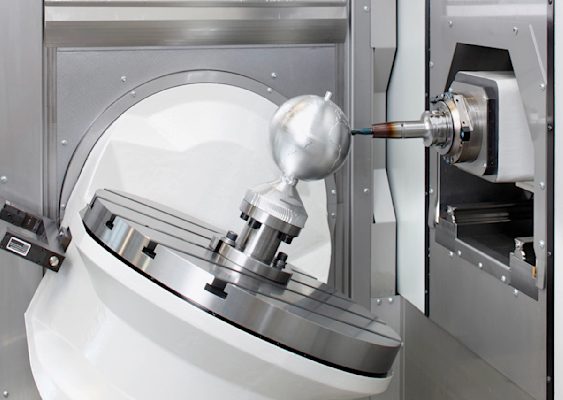

What is CNC machining best for? How engineers use it in practice
Need a part that fits right, performs reliably, and doesn’t take weeks to produce? CNC machining makes it happen. Engineers count on it for its tight tolerances, wide material compatibility, and fast turnarounds—no tooling required. Whether you’re prototyping or scaling up with production orders, CNC machining gives you full control over geometry, functionality, and surface finish.

What is CNC machining?
What is CNC machining and how does it work? This overview explains the basic principles and fundamental mechanics, along with the key benefits and limitations, of this subtractive manufacturing process.
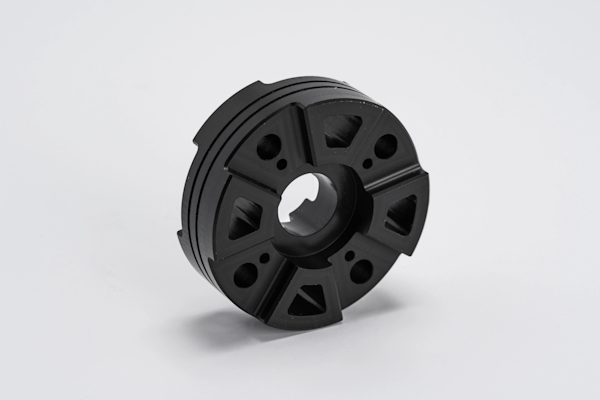

What is Delrin (POM-H) and what are its material properties?
What is Delrin and why is it unique? Delrin, or POM-H (homopolymer acetal), is a semi crystalline engineering thermoplastic used for CNC machining, 3D printing, and injection molding to produce durable, precision components. This article examines Delrin’s key properties and guidance for getting the most from the material.

What is CNC milling?
CNC milling is a subtractive manufacturing process used by engineers to source precision parts through outsourced CNC machining. This article explains how CNC milling machines work, what kinds of parts can be produced with milling, and design guidelines that help optimize parts for manufacturability.
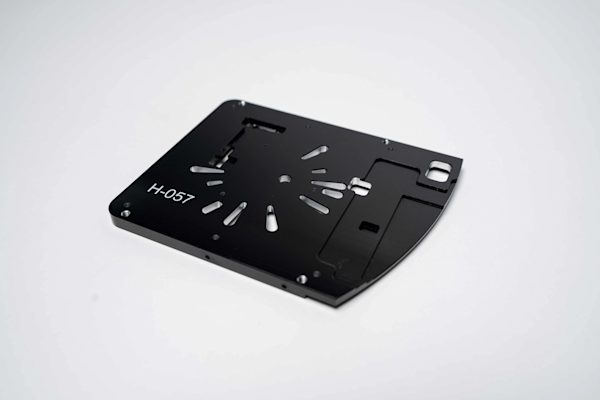

What is part marking for CNC machining? Practical tips for laser engraving, silk screening and more
How do you add logos, lettering, serial numbers and other customized designs to your custom parts? Part marking is a cost-effective way to give parts those extra identifying and/or cosmetic details. Learn the common part marking techniques on the market today, including laser engraving and silk screening.

Standard drill bit sizes for CNC machining
Use these conversion tables of standard drill bit sizes (metric, fractional inch, and wire gauge) common in CNC machining to reduce manufacturing costs from custom tooling.

3D printing vs. CNC machining: Which is better for prototyping and end-use parts?
When it comes to custom part production, choosing between 3D printing and CNC machining can be challenging. This guide breaks down the key differences between these popular manufacturing technologies, helping you decide which is best suited for prototyping, low-volume production, or functional end-use parts.
How to prepare a technical drawing for CNC machining
How do you prepare technical drawings for CNC machining and why are they important? Technical drawings are standard documents used in manufacturing to communicate technical requirements between the designer, engineering team, and the manufacturer. Clear drawings reduce ambiguity, speed up production, and help ensure parts are produced to the required specifications.

What are the types of surface finishes for CNC machining?
What surface finishes are available for CNC machining? Post-processing and surface finishes improve surface roughness, visual appearance, and wear resistance of metal parts. This guide covers the most common surface finishes for CNC-machined metal parts and how to choose the right one for engineered components.






